

#Virtual machines install#
With a Type 2 hypervisor, you manually create a VM and then install a guest OS in it. Type 2 hypervisors run as an application within a host OS and usually target single-user desktop or notebook platforms. Depending on your needs, you might create multiple VM templates for different purposes, such as software testing, production databases, and development environments. You can use one VM as a template for others, duplicating it to create new ones. Some management tools, like VMware’s vSphere, let you select a guest OS to install in the VM. Typically, you use a separate software product to create and manipulate VMs on the hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware (usually a server), taking the place of the OS. There are two primary types of hypervisors.
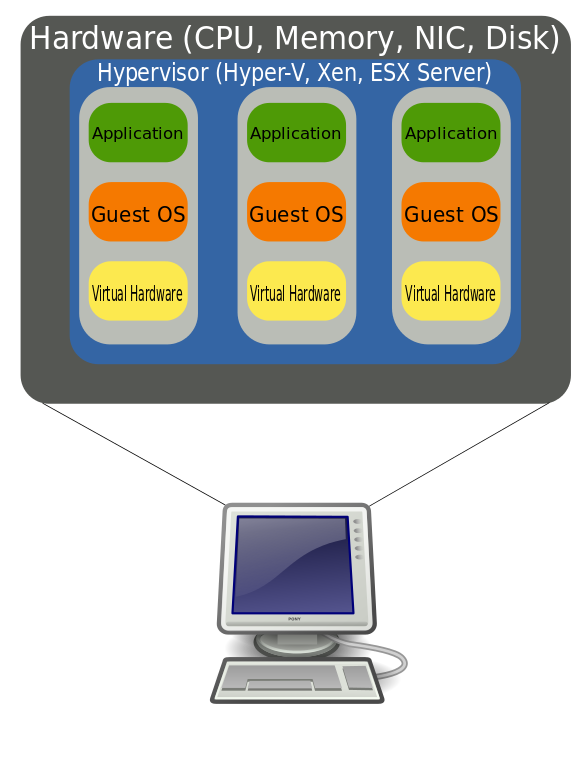
The hypervisor acts like a traffic cop of sorts, directing and allocating the bare metal’s resources to each of the various new virtual machines, ensuring they don’t disrupt each other.

Those resources include memory, RAM, storage, etc. Then, it can divide itself into several independent “virtual machines.”Įach of these new virtual machines can then run their own operating systems and applications independently while still sharing the original resources from the bare metal server, which the hypervisor manages. When a hypervisor is used on a physical computer or server, (also known as bare metal server), it allows the physical computer to separate its operating system and applications from its hardware.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
